Cảbon: Essential Element for Environmental and Technological Balance!

Introduction to Carbon
Carbon, represented by the symbol ‘C’ and possessing an atomic number of 6, is a fundamental element in the periodic table. It is not only one of the most abundant elements in the universe but also the backbone of life on Earth.
Carbon’s unique chemical properties allow it to form a diverse array of compounds, including the complex molecules that constitute living organisms.
The Role of Carbon in Life
Carbon’s ability to form stable bonds with many elements, including itself, makes it essential for the formation of long-chain molecules. These molecules, such as proteins, DNA, and carbohydrates, are crucial for life.
Proteins serve as the building blocks of cells, DNA stores genetic information, and carbohydrates provide energy. Without carbon, these complex molecules would not exist, and life as we know it would be impossible.
Carbon’s Chemical Properties
Atomic Structure
Carbon has four valence electrons, allowing it to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. This versatility is the basis for the diversity of carbon compounds.
The ability to form double and triple bonds, as well as chains and rings, contributes to the complexity of organic chemistry.
Allotropes of Carbon
Carbon exists in several different forms, known as allotropes, each with distinct physical properties. The most well-known allotropes are diamond, graphite, and graphene.
Diamond is renowned for its hardness and is used in cutting tools and jewelry. Graphite, which is soft and slippery, is used in pencils and as a lubricant.
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has remarkable electrical and mechanical properties, making it a promising material for future technologies.
The Carbon Cycle
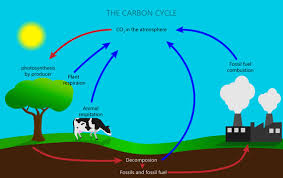
Source:asapeducate
Importance of the Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves through the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. This cycle is vital for maintaining the balance of carbon in the environment and supporting life.
Processes Involved in the Carbon Cycle
- Photosynthesis: Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and, using sunlight, convert it into organic matter. This process not only provides energy for the plants but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere.
- Respiration: Living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, release CO2 back into the atmosphere through respiration, where they convert organic matter into energy.
- Decomposition: When organisms die, decomposers break down their bodies, releasing carbon back into the soil and atmosphere.
- Combustion: The burning of fossil fuels and biomass releases stored carbon into the atmosphere as CO2.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
Fossil Fuel Combustion
The industrial revolution marked the beginning of large-scale combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas. This process releases significant amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Deforestation
The clearing of forests for agriculture and urban development reduces the number of trees available to absorb CO2 through photosynthesis. This exacerbates the accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Industrial Processes
Certain industrial processes, such as cement production, also release large amounts of CO2. These activities further disturb the natural carbon cycle.
The Role of Carbon in Climate Change
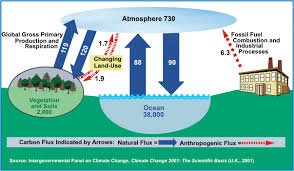
Source:timeforchange
Greenhouse Effect
CO2 is a greenhouse gas, meaning it traps heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. An increase in atmospheric CO2 levels enhances the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change. This has far-reaching consequences for weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems.
Mitigating Climate Change
- Reducing Emissions: Limiting the burning of fossil fuels and adopting renewable energy sources can help reduce CO2 emissions.
- Carbon Sequestration: Technologies and practices that capture and store carbon from the atmosphere can mitigate climate change. This includes reforestation and soil management techniques that increase carbon storage.
Carbon in Technology and Industry
Carbon Nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical structures with extraordinary strength and electrical conductivity. They have applications in nanotechnology, electronics, and materials science.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a strong and lightweight material used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries. It is made by weaving together strands of carbon and binding them with resin.
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is used in water purification, air filtration, and medical applications. Its porous structure allows it to adsorb a wide range of contaminants.
Future of Carbon Technologies
Sustainable Carbon Solutions
Developing sustainable technologies that utilize carbon efficiently is crucial for future progress. Innovations in carbon capture and storage, as well as the development of carbon-neutral fuels, are areas of active research.
Advancements in Materials Science
Continued research into carbon-based materials, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, holds the promise of revolutionizing various industries, from electronics to medicine.
Conclusion
Carbon is undeniably the backbone of life and a critical component of many industrial and technological processes.
Understanding its role in the natural world and the impact of human activities on the carbon cycle is essential for addressing environmental challenges and advancing sustainable technologies.
FAQs
What Is Carbon?
Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol ‘C’ and atomic number 6. It is essential for life on Earth, forming the basis of organic molecules such as proteins, DNA, and carbohydrates.
Why Is Carbon Important For Life?
Carbon’s unique ability to form stable bonds with many elements, including itself, allows it to create complex molecules that are the building blocks of life.
What Are The Allotropes Of Carbon?
The most well-known allotropes of carbon are diamond, graphite, and graphene. Each allotrope has distinct physical properties and uses.
How Does Carbon Cycle Through The Environment?
The carbon cycle involves processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion, which move carbon through the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms.
What Is The Greenhouse Effect?
The greenhouse effect is the process by which greenhouse gases, such as CO2, trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change.
How Do Human Activities Impact The Carbon Cycle?
Activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes increase atmospheric CO2 levels, disrupting the natural carbon cycle and contributing to climate change.
What Is Carbon Sequestration?
Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon to mitigate climate change. This can be achieved through reforestation, soil management, and technological solutions.
What Are Carbon Nanotubes?
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical structures with exceptional strength and electrical conductivity, used in various applications, including nanotechnology and materials science.
What Is Carbon Fiber?
Carbon fiber is a strong and lightweight material used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries. It is made by weaving together strands of carbon and binding them with resin.
What Are The Future Prospects Of Carbon-Based Technologies?
Future advancements in carbon-based technologies, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, hold the potential to revolutionize industries from electronics to medicine, while sustainable carbon solutions are essential for addressing environmental challenges.





